Mathematical Simulation Studies
In accordance with the basics described, GS offers Mathematical simulation studies for the following production units
for almost all types of glass:
- Glass Melting Furnaces
- Working Ends
- Forehearths
- Regenerators
- Recuperators

Regenerative end-port furnace for producing container glass
There are two types of projects:
1│SUPPORTING FURNACE DESIGN
- Furnace capacity
- Oxy fuel conversions
- Intensification of melting (e.g. electric boosting and bubbling)
- Design of a combustion system
- Batch charging
- Glass quality improvement
- Electric melting
- Design of the forehearth and glass homogeneity
- Ecology of melting
- Emission reduction
2│TROUBLESHOOTING
- Glass quality improvement
- Furnace lifetime extension
- Color change optimization
- Oxy fuel firing
- Burner design and set-up
Mathematical simulation studies were one of the key services when GS started in 1990 and GS is by far leading with this type of service.

Fiber furnace with oxy firing
Specific Benefits:
- Reduce specific energy consumption below 5,5 MJ/kg
- Reduce NOx emission below 1000 mg/m3
- Improve glass quality
- Improve furnace design, glass depth, length to width ratio
- Find optimal location of burners, electric boosting, barriers or steps
- Longer life time
- Reduction of CO2
- Reduce colour change time
- Reduce specific energy consumption below 3,5 MJ/kg
- Reduce NOx emission below 650 mg/m3
- Improve glass quality
- Improve furnace design, glass depth, length to width ratio
- Find optimal location of burners, electric boosting, barriers or steps and throat
- Longer life time
- Reduction of CO2
- Reduce colour change time
- Maximize pull
- Optimize size and design of the electric boosting
- Combustion chamber design to reflect oxy melting issues
- Flue gasses exhausts optimum positioning
- Fuel distribution for individual ports
- Bubbler line optimization
- Compare recuperative versus oxy firing
- Comparison of different designs
- Tailor-made furnace design proposal
- Comparison of different heating possibilities
- Hot top melters for high quality glasses
- Study of rare glass compositions and their impact on furnace design and operation
The cooperation with GS and the use of mathematical modeling was a fundamental boost to our evolution in electrical melting technology.
We are allowed to have confirmations about our ideas or comparisons within different hypotheses, and this gives us the confidence to move important steps ahead in this difficult field.
Example: Mathematical modeling of hybrid melter

GS H2EM (Horizontal Hot-top Electric Melter) design operating with 80% electric and 20% natural gas or hydrogen combustion. Specific consumption 2.5 MJ/kg.
Example: Mathematical modeling of all electric furnace
All electric furnace modelled for IWG Ingenieurbüro Wagenbauer
Example: Temperature overview of a float furnace
Furnace structure, gases flow, glass flow
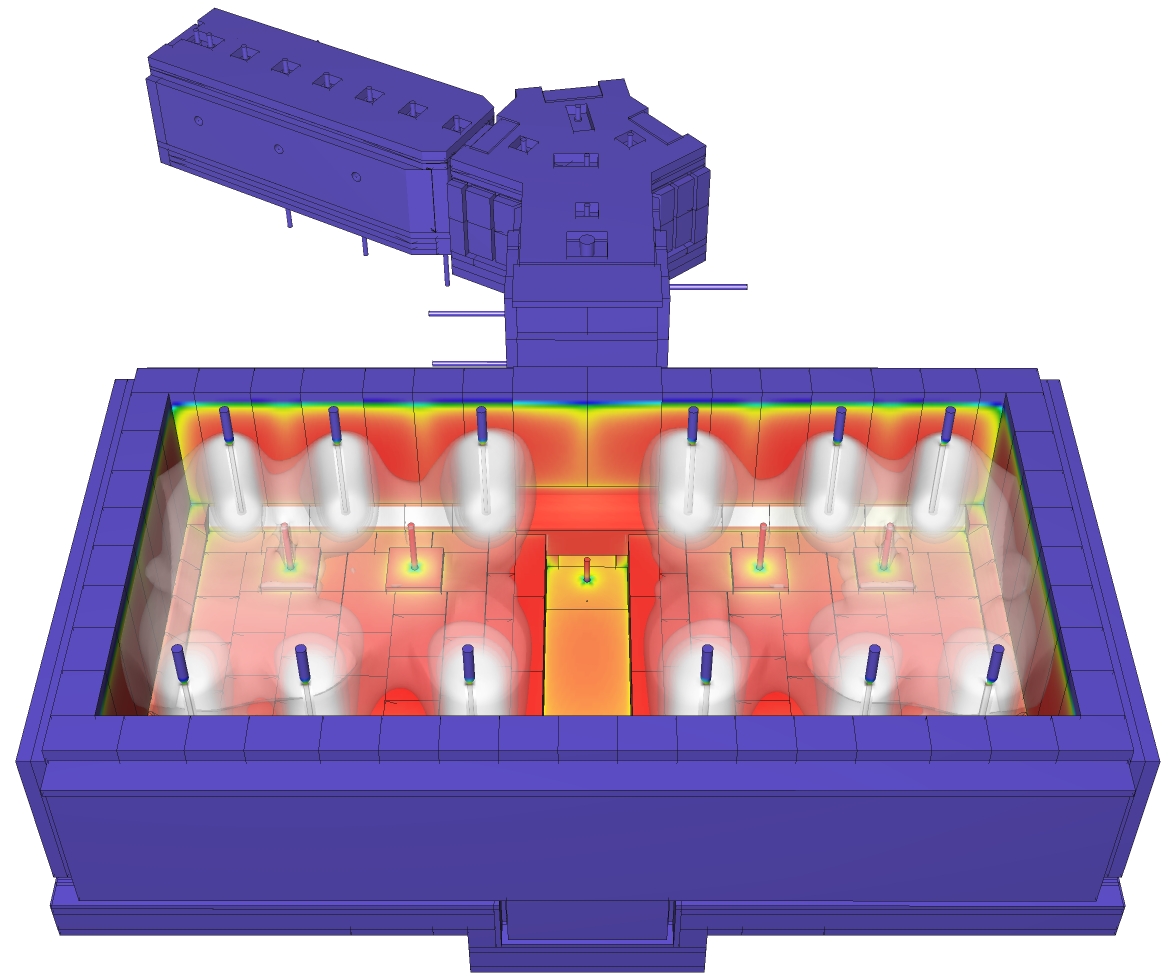
Example: Overview of a container glass furnace
Walls temperature, gases temperature, flow, batch and glass surface temperature
Example: Downstream tour through container glass channels
Walls and glass temperature, glass velocity
References:
GS has conducted more than 800 mathematical simulation studies worldwide.
Further Information:
-
Please contact us to receive more information, our latest presentation, or a quotation to purchase.